If a circle is divided into divided into four equal parts, then each part is known as a quadrant of a circle. The four circle quadrants each cover an angle of 90 degrees which adds up to a total of 360 degrees.
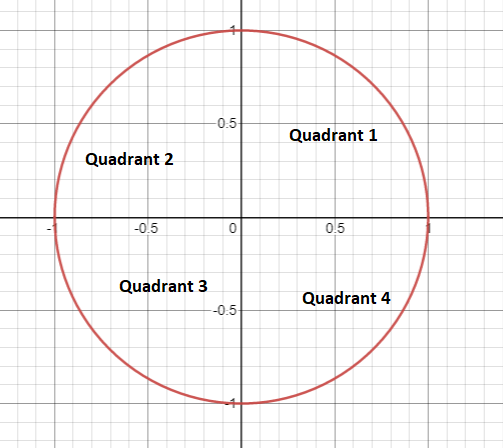
The quadrants are labeled the first quadrant, second quadrant, third quadrant, and fourth quadrant in an anti-clockwise manner as shown in the image below.
We now give the formulae for calculating the perimeter and area of a quadrant. Since quadrants are a quarter (one-fourth) of the circle, it is expected that the area and circular boundary of a quadrant be (1/4)th of that of a circle.
Formulae for a circular quadrant:
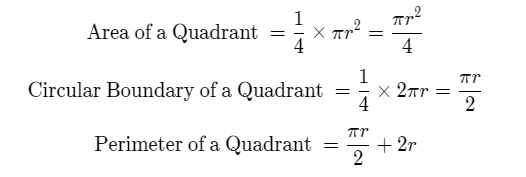
Note that when we calculate the perimeter, that is the entire boundary of the quadrant we add 2 times the radius to the circular boundary.
This is because the quadrant consists of a circular part and 2 straight lines whose length is equal to the radius.
Example 1:
Suppose that a circular cake having a radius of 10cm is cut into four equal parts. Calculate the area and perimeter of a single quadrant of the circle.
Solution: We know that π = 22/7 and we are given r = 10cm. We now simply apply the formulae stated above.
Area of a Quadrant = πr2/4 = 22/7 * 100/4 = 78.57 cm2.
Perimeter of a Quadrant= πr/2+ 2r = 22/7 * 10/2 + 20 = 15.71 + 20 = 35.71cm.
Example 2:
Given a quadrant having a radius of 35 cm, calculate its area and the length of the circular arc/circular boundary of the quadrant.
Solution: We know that r = 35cm.
Area of a Quadrant = πr2/4 = 22/7 * 352/4 = 962.5 cm2.
Length of circular arc = πr/2 = 22/7 * 25/2 = 55cm.
The Quadrant Circle in Trigonometry:
The unit circle having a radius equal to 1 plays an important role in the definition of the trigonometric ratios of sine and cosine. When we draw the radius at a particular angle θ it intersects the circle at some point P.
The y-coordinate of that point is defined to be sin(θ) and the x-coordinate is defined to be cos(θ).
Depending on the quadrant in which the angle lies we can predict whether the sine or cosine of that angle will be positive or negative.
For example, if θ lies in the second quadrant then since the x-coordinate here is negative and the y-coordinate positive we conclude that cos(θ) takes a negative value and sin(θ) takes a positive value.