Sometimes in a grouped frequency distribution, there is a gap between the upper limit of a class and the lower limit of the next class interval.
In such a case, we can correct the class limits to make sure that the upper limit of any class and the lower limit of the next class are equal. The new class limits obtained by the correction procedure are called the class boundaries.
How to Calculate Class Boundaries:
- Find the difference between the upper limit of the class and the lower limit of the next class. Let us call this difference to be d.
- Divide the resulting difference by 2. This gives us the correction factor, that is, correction factor = d/2.
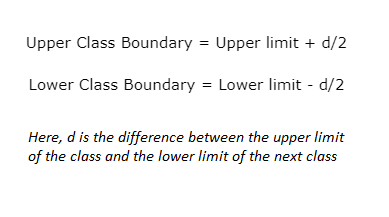
- Calculate the new class boundaries using the formula,
Upper Class Boundary = Upper limit + d/2
Lower Class Boundary = Lower limit – d/2
Let us try to understand this by looking at some examples.
Example 1:
Consider the following inclusive type of frequency distribution,
| Class Intervals | Frequency |
| 0-9 | 5 |
| 10-19 | 15 |
| 20-29 | 16 |
| 30-39 | 17 |
| 40-49 | 14 |
We now convert the class limits into class boundaries as follows,
Step 1: Calculate the difference between the upper limit of the class and the lower limit of the next class interval,
d = 10-9 = 1
Step 2: Divide the difference by 2 to calculate the correction factor.
d/2 = (10-9)/2 = 1/2 = 0.5
Step 3: Calculate the class boundaries by using the formula,
Upper Class Boundary = Upper limit + d/2
Lower Class Boundary = Lower limit – d/2
For example, consider the class 20-29. Then we have that,
Upper Class Boundary = Upper limit + d/2 = 29 + 0.5 =29.5
Lower Class Boundary = Lower limit – d/2 = 20 – 0.5 = 19.5
In this way, we obtain the class boundaries for all the classes as shown below,
| Class Intervals | Frequency |
| 0-9.5 | 5 |
| 9.5-19.5 | 15 |
| 19.5-29.5 | 16 |
| 29.5-39.5 | 17 |
| 39.5-49.5 | 14 |
Example 2:
We are given the following grouped frequency distribution,
| Class Intervals | Frequency |
| 20-24 | 13 |
| 25-29 | 22 |
| 30-34 | 8 |
| 35-39 | 31 |
| 40-44 | 45 |
The correction factor is equal to,
d/2 = (25 – 24)/2 = 1/2 = 0.5
We calculate the class boundaries as shown below,
| Class Intervals | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Class Boundaries | Frequency |
| 20-24 | 20-0.5 = 19.5 | 24+0.5 = 24.5 | 19.5 – 24.5 | 13 |
| 25-29 | 25-0.5 = 24.5 | 29+0.5 = 29.5 | 24.5 – 29.5 | 22 |
| 30-34 | 30-0.5 = 29.5 | 34+0.5 = 34.5 | 29.5 – 34.5 | 8 |
| 35-39 | 35-0.5 = 34.5 | 40+0.5 = 39.5 | 34.5 – 39.5 | 31 |
| 40-44 | 40-0.5 = 39.5 | 44+0.5 = 44.5 | 39.5 – 44.5 | 45 |
Remarks:
- The average of the upper and lower class boundaries gives us a value close to the midpoint of the class interval.
- Finding the class boundaries allows us to convert the inclusive type of class intervals to the exclusive type of class intervals.
- Converting into the exclusive type of class intervals is important because we can then calculate the mode and the median of the grouped frequency distribution.