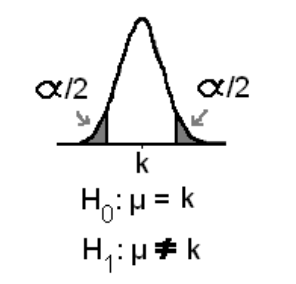
The Zalpha/2 (Zα/2) refers to the critical table value we obtain when conducting a two-tailed Z test at the α% level of significance. The Zα/2 value is important because it is used to decide whether we should accept the null hypothesis or reject the null hypothesis.
Use of Zα/2:
If the absolute value of the calculated Z statistic value exceeds Zα/2 (Zalpha/2 or Za/2) in the two-tailed test then we reject the null hypothesis. If the absolute value of the calculated Z statistic value does not exceed Zα/2 (Zalpha/2 or Za/2) then we accept the null hypothesis.
This is because Zα/2 marks out the two critical regions at α% level of significance in the two-tailed test as shown in the below image.
Example of how to find Zalpha/2 (Zα/2):
- Given the level of significance α, calculate α/2.
- Find the Z value corresponding to a probability of α/2 in the Z table.
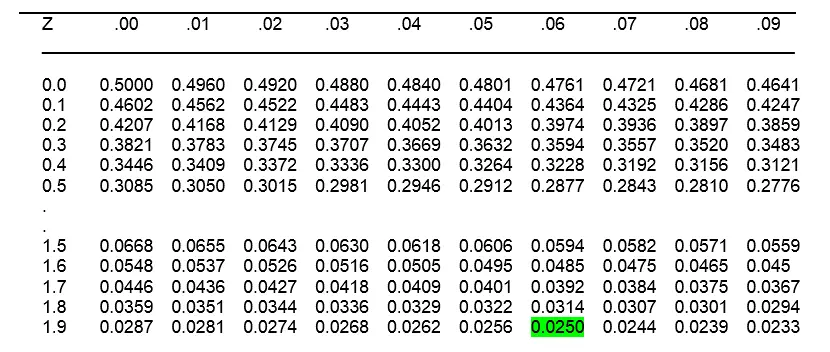
- For example if α=5% we find that for 0.05/2=0.025 in the below table we get that Zα/2=1.96.